The Integrated Disability Evaluation System (IDES)

When a service member develops a medical condition that makes them unable to perform their duties in the military, they are referred to the Integrated Disability Evaluation System (IDES).
The Integrated Disability Evaluation System was developed in 2009 to bridge the gap between the DoD Disability Process and the VA Disability Process. The goal of the IDES is to simplify and streamline Military Disability by combining the two disability processes and having the VA and the DoD work together and share information.
Before 2009, the DoD used only the Legacy Disability Evaluation System (LDES), which consists solely of the DoD’s Disability Process without any involvement of the VA. Today, only the IDES is used unless the service member specifically requests to go through the LDES or unless there are special circumstances that require the LDES instead.
Through the Integrated Disability Evaluation System, the VA and DoD work together to determine which medical conditions qualify for service-connection and Unfit for Duty (required for DoD only). For the conditions that qualify, the VA assigns disability ratings which determine the benefits the service member will receive upon discharge.
Below, we give the steps of the Integrated Disability Evaluation System with a basic discussion of each of the steps. For more in-depth details of each part, click on the links throughout the discussion.
Do note that the time frames listed below are ONLY estimated goals established by the DoD and VA and do not always reflect actual wait times. Actual wait times depend on the completeness of the claim submitted, the amount of claims being processed in that office at that time, etc. Some are processed faster, some slower.
The current goal as of November 2022 is for the entire IDES process to take no more than 180 days from referral to completion for at least 80% of all cases.
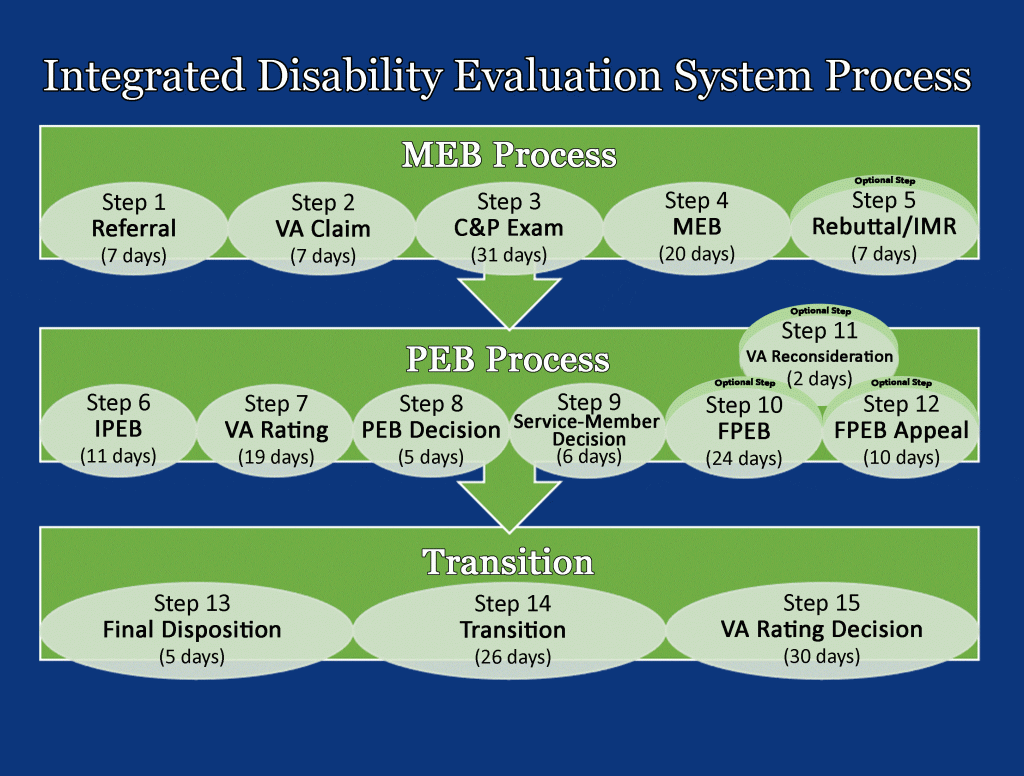

Step 1: Referral. When a service member develops a medical condition that their physician believes will not heal enough for them to be able to return to full duty within one year, they are referred to the Medical Evaluation Board (MEB), begin the MEB Process, and are assigned a DoD PEBLO (Physical Evaluation Board Liaison Officer) and a VA Military Services Coordinator (MSC) to assist them throughout the Integrated Disability Evaluation System.

Step 2: VA Claim. After the service member is referred to the MEB, their MSC helps them submit a VA Disability Claim.

Step 3: C&P Exam. Once the VA Disability Claim is submitted, the service member goes to the VA for a C&P Exam(s).

Step 4: MEB. At this point in the Integrated Disability Evaluation System process, the results from the C&P Exam are returned to the PEBLO, and the case is forwarded to the Medical Evaluation Board (MEB). The MEB reviews the service member’s conditions and compiles a report that summarizes the history of the service member’s medical conditions from their beginning up through the exam. This report is called a “Narrative Summary” or “NARSUM.” The MEB also determines the medical acceptability of each of the service member’s conditions. If none of the conditions are medically unacceptable, the service member is returned to duty. If at least one of the conditions is medically unacceptable, the MEB forwards the case to the PEB after the service member’s review.
Step 5: Rebuttal/IMR (optional). After the service member reviews the MEB’s findings, they have the option to request an impartial medical review (IMR) and/or submit a rebuttal. The IMR is conducted by a physician outside the scope of the MEB. This physician reviews the MEB’s findings and counsels the service member on whether or not the findings adequately represent their conditions. If the service member wishes to submit a rebuttal, the MEB will review the service member’s arguments and the IMR, if applicable, and will make a final decision on the case. This decision is then forwarded to the IPEB.

Step 6: IPEB. Once the Informal Physical Evaluation Board (IPEB) receives the MEB’s decision, the PEB Process begins. The IPEB determines which of the service member’s conditions qualify for DoD Disability. To qualify, conditions must be Service-Connected and make the service member Unfit for Duty.

Step 7: VA Rating. Once the IPEB determines which conditions make the service member Unfit for Duty, they send their decision to the VA. There must be at least one unfitting condition for the case to continue. If none of the conditions are unfitting, then the service member is returned to duty, and the Integrated Disability Evaluation System process ends. If the case is forwarded to the VA, then the VA assigns a Military Disability Rating to every service-connected condition the service member has. The VA is the official Rating Authority for both VA Disability and DoD Disability.

Step 8: PEB Decision. Once the VA’s Rating Decision is made, it is sent back to the IPEB. The IPEB uses the VA’s ratings as the official ratings for DoD Disability for the service member’s unfitting conditions (reminder: the DoD only gives disability for conditions that make a service member Unfit for Duty).

Step 9: Service-Member Decision. The PEB’s decision is sent to the PEBLO who then discusses it with the service member. The service member then has the chance to accept it or request a Formal PEB.

Step 10: FPEB Appeal (optional). If the service member does not agree with the PEB’s decision of which conditions are unfitting, they can request to have the Formal Physical Evaluation Board (FPEB) review their case. The FPEB then reviews the case and makes a decision on the unfitting conditions.

Step 11: VA Reconsideration (optional). If the service member does not agree with the VA’s Rating Decision, they can submit for reconsideration. The VA will re-examine the case and make a final rating decision. The FPEB will then apply the updated VA ratings to the unfitting conditions.

Step 12: FPEB Appeal (optional). If the service member doesn’t agree with the FPEB’s decision, they can submit an appeal. The case is then reviewed and a final decision made. If the decision is that none of the service member’s conditions are unfitting, then the service member is returned to duty. If at least one of the conditions is unfitting, then the case is sent to the branch Secretary for final disposition.

Step 13: Final Disposition. Once the service member agrees with the PEB’s decision or a final decision is made on an appeal, the Secretary of the military branch reviews and approves the case.

Step 14: Transition. With the Secretary’s approval, the service member is either placed on TDRL, medically separated, or medically retired from the military.

Step 15: VA Rating Decision. Thirty days after the service member is discharged from the military or placed on TDRL, the VA officially publishes its Rating Decision, and the Integrated Disability Evaluation System process ends.
That’s it. The Integrated Disability Evaluation System (IDES) definitely saves the veteran time and effort by allowing both systems to be processed simultaneously with less hassle. The Integrated Disability Evaluation System also allows the veteran to receive both DoD Disability and VA Disability within 1 month of separating from the military, thus ensuring that veterans are receiving their essential compensation as soon as possible.
Return to Top
Integrated Disability Evaluation System (IDES) FAQs
What is the Integrated Disability Evaluation System (IDES)?
The Integrated Disability Evaluation System (IDES) combines both the DoD and the VA disability systems into one streamlined process to ensure that service members are able to receive their essential disability benefits as soon as possible upon separation.
How long does the Integrated Disability Evaluation System (IDES) take?
The Integrated Disability Evaluation System (IDES) usually takes roughly 5-6 months from referral to the MEB until separation and the start of VA disability benefits.
Am I eligible for DoD Disability?
You are eligible for disability benefits from the DoD if you have one or more medical conditions caused by your military service (service-connected) that also make you Unfit for Duty.
How do I apply for DoD Disability?
You do not apply for DoD Disability, but are instead referred to the Medical Evaluation Board by your military physician. This referral starts the DoD Disability Process.
Am I eligible for VA Disability?
You are eligible for disability benefits from the VA if you have one or more medical conditions that you can prove are service-connected.
How long does it take to receive my disability benefits?
You will receive your first payment within 1-2 months after discharge.
What is the Medical Evaluation Board?
The Medical Evaluation Board (MEB) is the first board in the IDES. They review your conditions and forward the conditions they feel are medically unacceptable to the Physical Evaluation Board for an Unfit for Duty determination.
What is the Physical Evaluation Board?
The Physical Evaluation Board (PEB) is the final Board before a medical discharge from the military. The PEB reviews your conditions and makes the final determination on which conditions make you Unfit for Duty and assign them the ratings issued by the VA.
What if I don't agree with the PEB's decision?
You have the right to appeal the PEB's decision. If you appeal, your case will then be reviewed by the Formal Physical Evaluation Board (FPEB).


